Function
Functions are used to take some input data as arguments and return a result of a specified data type.
Overview
A function behaves much like methods in many programming languages, they take inputs as arguments and return a result. The arguments to a function are defined as input data, they have a name and a Java class (or primitive) type.
Functions can optionally define internal values, which are similar to local variables. They are useful for extracting values from a complex input or deriving values through some function calls in order to keep the function logic clear and concise.
When defining a function the return type must be specified in its output data field. The value returned in the function’s body must match the return type.
A simple example function is shown below:
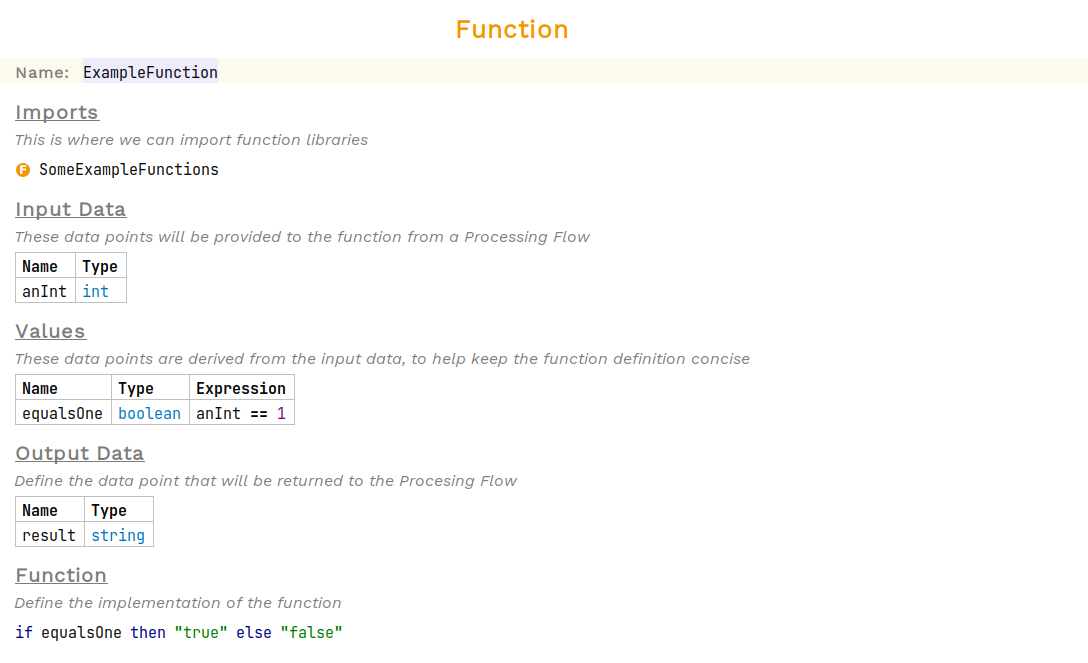
The function takes a single integer as it’s input data, anInt. The input data anInt is used to derive a boolean value equalsOne which is later used in an if expression in the function body to determine whether to return "true" or "false".
Input Data
Input data can refer to Java primitive types and Java classes.
When referring to a Java class, a Java Record Link is automatically generated and imported. The link is required to bridge the Java class with an equivalent Kernel F record, which can be used in expressions.
|
Values
Multiple internal values can be defined within a function. Values can reference input data and other values (providing they are defined before them).
Values have a name, type and expression. The expression must produce a result that matches the value’s type.
Function
The last section of the function definition is the function itself. It may reference the input data or values defined above and must return a value matching the output data type.