Dynamic Processing Settings Overview
Overview
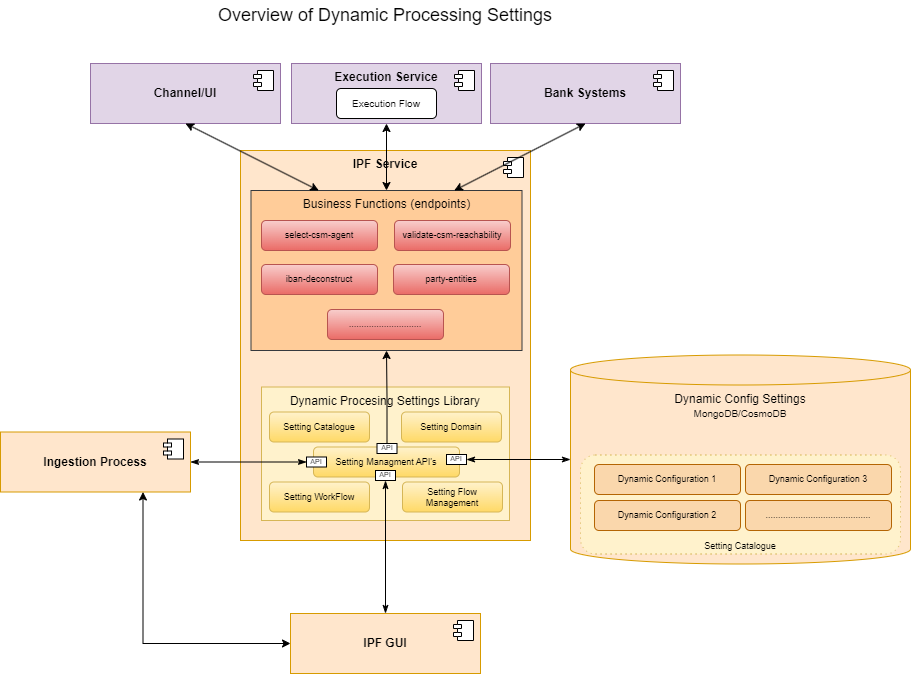
The diagram above depicts the use of DPS in the overall context of the IPF implementation. DPS can be implemented within an IPF Service as a library that facilitates the CRUD operation on the underlying MongoDB collections called the Dynamic Config Settings. Settings can be ingested through IPF GUI, local file directories or AWS S3 bucket.
Business functions using DPS
The business functions invoked from these process flows that can be deployed in different processing services (e.g. Working Days Service). Service guidelines should be followed on whether Dynamic Processing Settings can be used directly within the flows or other APIs provided by the service are used to interact with Dynamic configurations (e.g. Domain APIs provided by CSM Reachability Service).
CSM Reachability Service
The CSM Reachability Service is one example of a business function using DPS. Within this service, DPS has been implemented for managing data such as Agent Settings, Agent Settlement Settings, CSM Participants, and Processing Entities. CSM Reachability Service incorporates DPS alongside its core reachability functions and additional features.
Working Days Service
Calendar data types are defined within the settings catalogue, and DPS is embedded in the Working Days Service application as a supporting feature, enabling dynamic management of calendar-related settings.
Payment Status Notification
This application consumes domain events and, based on filter and notification configurations, generates payment status notifications in the pain.002 JSON format, which are published to a Kafka topic. Internally, it uses DPS for managing filter and notification configurations. The configuration is pluggable, meaning users can replace the Dynamic Setting Configuration with a HOCON configuration if desired.
Components of DPS
| 1 | Settings Catalogue
|
| 2 | Settings Domain
|
| 3 | Settings Workflow
|
| 4 | Settings Management API
|