Private Functions
Private Functions are reusable bodies of code that take zero or more arguments and give a single output.
Overview
A function behaves much like methods in many programming languages, they take inputs as arguments and return a result. The arguments to a function are defined as input data, they have a name and a Kernel F record (or primitive) type.
Functions can optionally define internal values, which are similar to local variables. They are useful for extracting values from a complex input or deriving values through some function calls in order to keep the function logic clear and concise.
When defining a function, the return type must be specified in its output data field. The value returned in the function’s body must match the return type.
A simple example function is shown below:
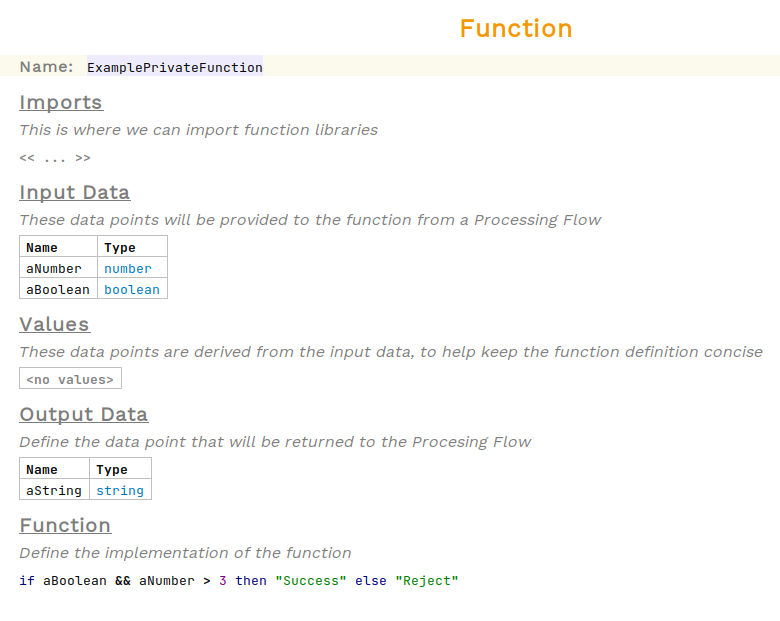
Differences between Functions and Private Functions
While Private Functions look similar in shape to Function nodes, they are different.
Here is a list of the main differences between them
Difference |
Function |
Private Function |
Data Types |
Both input and output are Java types |
Both input and output are Kernel F Records/Primitives |
Usage Locations |
Calling a Function is an Action within a flo |
Called from the bodies of Decisions, Validations, Functions or other Private Functions |
Intended Use |
For mapping to business data within the DSL |
For writing logic withing the DSL |