ISO20022 Concepts
ISO20022 was created to standardise information exchange between different parties involved in financial services. While ISO20022 covers many areas within financial services, e.g. securities, trade finance, cards and foreign currency exchange, IPF support is focused on the payments area.
| If you are new to ISO20022 then we recommend reading the free SWIFT ebook ISO20022 for Dummies to familiarise yourself. |
Meta-Model
The ISO20022 model comprises four levels, based on the first four levels of the Zachmann Enterprise Architecture Framework.
| Level | Purpose |
|---|---|
Scope |
Achieving a thorough understanding of the objectives of the business area, its relevant processes and the roles that involved parties play in them. |
Conceptual |
Formalising the semantics and discovering the communication and interaction requirements of the business processes by defining the business transactions, business activities and message choreographies related to the business processes. |
Logical |
Creating a precise description of the messages and systems, without regard to how they will be implemented, focusing on message definitions, message building blocks and message elements. |
Physical |
Creating a precise description of the messages and systems in a technology that can be used for implementation. |
Meta Model Overview
The below diagram shows some primary concepts and relationships within the model, note that the in addition to being split by level, concepts are also split between "static" and "dynamic" regions, this further describes the principle of having a standard data dictionary of objects, and using those objects within the context of various business processes / message exchanges.
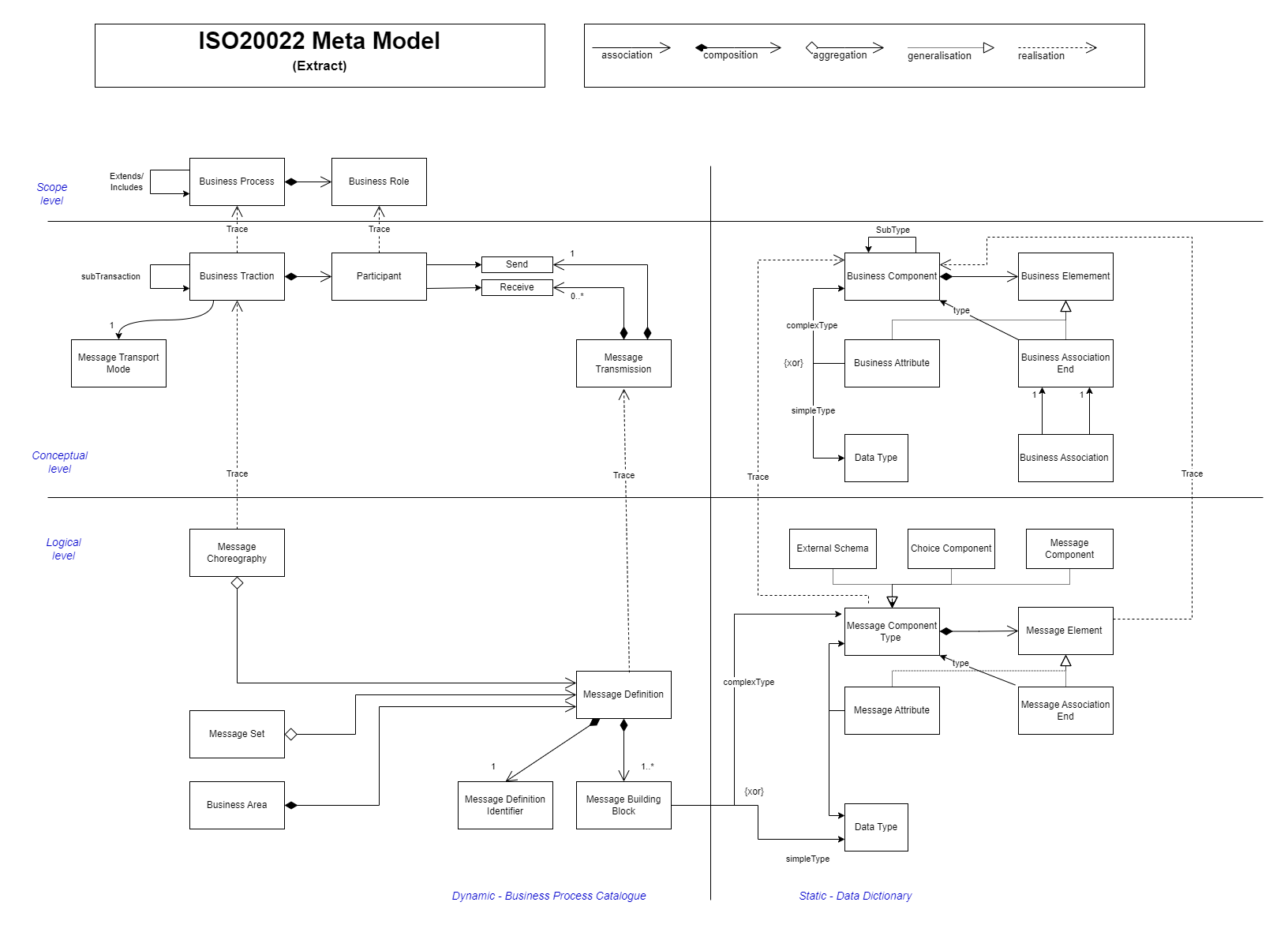
Meta-Model Concepts
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
The Message Model refers to the part of the meta-model dealing with Message Definitions |
|
The Business Model refers to the part of the meta-model dealing with Business Processes |
|
A Business Area is a domain under which Message Definitions and other concepts are grouped, e.g. Payment Initiation |
|
A Message Definition is a single type of message that can be exchanged, e.g. |
|
A Message Component is a complex type to be used in one or more Message Definitions, it may reference other Message Components or Message Elements, e.g. |
|
A Message Element is a simple type attribute of a Message Component, e.g. |
|
A business component is a more general representation of a standard type, such as an Account. In reality, it is a superset/archetype of the various representations of Account from the Message Components such as |
|
A simple type attribute of a Business Component, e.g. Account.name |
|
A trace is a physical link from one abstraction level of the model to another. Aside from the E-Repo this information is seen in the Message Definition Reports |
Glossary
The term ISO20022 is overloaded and often too vague, especially when attempting to deal with multiple aspects such as the specification, the data, the meta-model and its concepts.
Below is a set of informal definitions for various primary concepts
ISO20022
Term |
Description |
ISO20022 is a single standardised approach (methodology, process, repository) to be used by all financial standards initiatives |
|
The ISO20022 Registration Authority is a group that provides governance for the technical representation of the published ISO20022 repository artefacts. For our purposes they are the maintainers of www.iso20022.org, which supplies XSDs, E-Repository and EMF format ISO20022 Meta-Model. |
|
The Meta-Model consists of concepts, rules, types and relationships that formally map the interaction for Financial Message exchange. There are around 100 concepts in the model, which include message exchanges, business activities and the roles of various parties within an activity. |
Technical formats
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
EMF is a language modelling format (similar to MPS) to allow the definition of Meta-Models. The ISO2002 Meta-Model is described in this format, and published by the RA. An EMF model is represented in a *.ecore file format. |
|
The E-repo is a 100Mb binary file containing all the ISO20022 data in the EMF Meta-Model format. It is represented as a *.iso20022 file format. |
|
MDRs are multipart reference documents that are published by the ISO20022 RA that describe various Message Choreographies and Message Definitions. For each Business Area They are represented as a set of *.docx, *.pdf, *.xls file formats. |
|
XSDs are a standard format for expressing a schema, XSDs are provided for each Message Definition by the ISO20022 RA. They are represented as *.xsd file format. |
Business Model
The ISO20022 Business Model refers to part of the ISO20022 Meta-Model related to Business Process and Business Components, a higher conceptual level than the more frequently used Message Model. It is described in greater detail within the documentation pages for the ISO2022-Meta component.
The IPF ISO20022 Model provides a Java pojo implementation of the Business Model for reference and understanding, though the focus of our current efforts are toward the Message Model implementation.
All business component Pojos can be found within the following packages
com.iconsolutions.iso20022.business.components
within the following artifact
<dependency>
<groupId>com.iconsolutions.iso20022.model</groupId>
<artifactId>business-model</artifactId>
<version>${icon-iso20022-model.version}</version>
</dependency>Message Model
The ISO20022 Message Model refers to part of the ISO20022 Meta-Model related to Message Definitions and Message Components. Instances of these are commonly described in XSDs provided by ISO20022. Full details of the various concepts of the Message Model can be found within the ISO20022-Meta documentation.
The rest of this documentation relates to the Java implementation of the subset of Message Definitions used by IPF, this implementation includes serialisation and validation / constraints as described within features section.
Java Message Definitions
All Message Definitions are generated into the following package:
com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.definitions
Below is part of a Pain.001.01.09 Message Definition. Generally speaking it is a Pojo with additional enhancements such
as Lombok builders, full descriptions as code comments, additional "Message Rules" (on top of the XSD rules) applied as
JSR303 annotations.
package com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.definitions.payments_initiation.pain001;
/*Generated by MPS */
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.meta.annotations.MessageDefinition;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Data;
import com.iconsolutions.ipf.payments.domain.annotation.Description;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.media.Schema;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.definitions.payments_initiation.pain001.jsr303.SupplementaryDataRule;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.meta.validation.level.MessageRule;
import java.io.Serializable;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.meta.annotations.MetaData;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.payment.group_header85.GroupHeader85;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size;
import java.util.List;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.payment_instruction.payment_instruction30.PaymentInstruction30;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.technical.supplementary_data1.SupplementaryData1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
*
* Scope
* The CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is sent by the initiating party to the forwarding agent or debtor agent. It is used to request movement of funds from the debtor account to a creditor.
* Usage
* The CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can contain one or more customer credit transfer instructions.
* The CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is used to exchange:
* - One or more instances of a credit transfer initiation;
* - Payment transactions that result in book transfers at the debtor agent or payments to another financial institution;
* - Payment transactions that result in an electronic cash transfer to the creditor account or in the emission of a cheque.
* The message can be used in a direct or a relay scenario:
* - In a direct scenario, the message is sent directly to the debtor agent. The debtor agent is the account servicer of the debtor.
* - In a relay scenario, the message is sent to a forwarding agent. The forwarding agent acts as a concentrating financial institution. It will forward the CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message to the debtor agent.
* The message can also be used by an initiating party that has authority to send the message on behalf of the debtor. This caters for example for the scenario of a payments factory initiating all payments on behalf of a large corporate.
* The CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can be used in domestic and cross-border scenarios.
* The CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message must not be used by the debtor agent to execute the credit transfer instruction(s). The FIToFICustomerCreditTransfer message must be used instead.
*/
@MessageDefinition(value = "pain.001.001.09")
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "CustomerCreditTransferInitiationV09", propOrder = {"grpHdr", "pmtInf", "splmtryData"})
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@Data
@Description("Scope\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is sent by the initiating party to the forwarding agent or debtor agent. It is used to request movement of funds from the debtor account to a creditor.\r\nUsage\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can contain one or more customer credit transfer instructions.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is used to exchange:\r\n- One or more instances of a credit transfer initiation;\r\n- Payment transactions that result in book transfers at the debtor agent or payments to another financial institution;\r\n- Payment transactions that result in an electronic cash transfer to the creditor account or in the emission of a cheque.\r\nThe message can be used in a direct or a relay scenario:\r\n- In a direct scenario, the message is sent directly to the debtor agent. The debtor agent is the account servicer of the debtor.\r\n- In a relay scenario, the message is sent to a forwarding agent. The forwarding agent acts as a concentrating financial institution. It will forward the CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message to the debtor agent.\r\nThe message can also be used by an initiating party that has authority to send the message on behalf of the debtor. This caters for example for the scenario of a payments factory initiating all payments on behalf of a large corporate.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can be used in domestic and cross-border scenarios.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message must not be used by the debtor agent to execute the credit transfer instruction(s). The FIToFICustomerCreditTransfer message must be used instead.")
@Schema(description = "Scope\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is sent by the initiating party to the forwarding agent or debtor agent. It is used to request movement of funds from the debtor account to a creditor.\r\nUsage\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can contain one or more customer credit transfer instructions.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message is used to exchange:\r\n- One or more instances of a credit transfer initiation;\r\n- Payment transactions that result in book transfers at the debtor agent or payments to another financial institution;\r\n- Payment transactions that result in an electronic cash transfer to the creditor account or in the emission of a cheque.\r\nThe message can be used in a direct or a relay scenario:\r\n- In a direct scenario, the message is sent directly to the debtor agent. The debtor agent is the account servicer of the debtor.\r\n- In a relay scenario, the message is sent to a forwarding agent. The forwarding agent acts as a concentrating financial institution. It will forward the CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message to the debtor agent.\r\nThe message can also be used by an initiating party that has authority to send the message on behalf of the debtor. This caters for example for the scenario of a payments factory initiating all payments on behalf of a large corporate.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message can be used in domestic and cross-border scenarios.\r\nThe CustomerCreditTransferInitiation message must not be used by the debtor agent to execute the credit transfer instruction(s). The FIToFICustomerCreditTransfer message must be used instead.")
@SupplementaryDataRule(groups = MessageRule.class)
public class CustomerCreditTransferInitiationV09 implements Serializable {
/**
* Set of characteristics shared by all individual transactions included in the message.
*/
@MetaData(fullName = "GroupHeader")
@XmlElement(name = "GrpHdr", required = true)
@NotNull
@Valid
protected GroupHeader85 grpHdr;IPF Supported Message Definitions
At the time of writing the current "supported" message definitions for IPF include:
| Message Definition Identifier | Message Definition |
|---|---|
acmt.023.001.04 |
IdentificationVerificationRequestV04 |
acmt.024.001.04 |
IdentificationVerificationReportV04 |
admi.002.001.01 |
MessageRejectV01 |
admi.004.001.02 |
SystemEventNotificationV02 |
admi.007.001.01 |
ReceiptAcknowledgementV01 |
admi.011.001.01 |
SystemEventAcknowledgementV01 |
camt.019.001.07 |
ReturnBusinessDayInformationV07 |
camt.025.001.06 |
ReceiptV06 |
camt.026.001.07 |
UnableToApplyV07 |
camt.027.001.07 |
ClaimNonReceiptV07 |
camt.028.001.09 |
AdditionalPaymentInformationV09 |
camt.029.001.09 |
ResolutionOfInvestigationV09 |
camt.052.001.08 |
BankToCustomerAccountReportV08 |
camt.054.001.10 |
BankToCustomerDebitCreditNotificationV10 |
camt.055.001.08 |
CustomerPaymentCancellationRequestV08 |
camt.056.001.08 |
FIToFIPaymentCancellationRequestV08 |
camt.087.001.06 |
RequestToModifyPaymentV06 |
head.001.001.02 |
BusinessApplicationHeaderV02 |
pacs.002.001.10 |
FIToFIPaymentStatusReportV10 |
pacs.003.001.08 |
FIToFICustomerDirectDebitV08 |
pacs.004.001.09 |
PaymentReturnV09 |
pacs.007.001.09 |
FIToFIPaymentReversalV09 |
pacs.008.001.08 |
FIToFICustomerCreditTransferV08 |
pacs.009.001.08 |
FinancialInstitutionCreditTransferV08 |
pacs.028.001.03 |
FIToFIPaymentStatusRequestV03 |
pain.001.001.09 |
CustomerCreditTransferInitiationV09 |
pain.002.001.10 |
CustomerPaymentStatusReportV10 |
pain.007.001.09 |
CustomerPaymentReversalV09 |
pain.008.001.08 |
CustomerDirectDebitInitiationV08 |
pain.013.001.07 |
CreditorPaymentActivationRequestV07 |
pain.014.001.07 |
CreditorPaymentActivationRequestStatusReportV07 |
Message Definitions are comprised of Message Components.
Message Components
All Message Components are generated into the following package
com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.<subpackage>
Below is an except of a GroupHeader85 Message Component. As with Message Definitions, Message Components are Java
beans with additional enhancements such Lombok builders, full descriptions as code comments,
additional "Message Rules" (on top of the XSD rules) applied as JSR303
annotations, and metadata relating the Message Components to Business Components.
package com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.payment.group_header85;
/*Generated by MPS */
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.meta.annotations.MessageComponent;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Data;
import com.iconsolutions.ipf.payments.domain.annotation.Description;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.media.Schema;
import java.io.Serializable;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.meta.annotations.MetaData;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Size;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XmlJavaTypeAdapter;
import com.iconsolutions.ipf.payments.domain.jaxb.adapter.OffsetDateTimeFromIsoDateTimeXmlAdapter;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSchemaType;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
import jakarta.validation.Valid;
import java.util.List;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.technical.authorisation1_choice.Authorisation1Choice;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Pattern;
import jakarta.validation.constraints.Digits;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.party_identification_information.party_identification135.PartyIdentification135;
import com.iconsolutions.iso20022.message.components.organisation.branch_and_financial_institution_identification6.BranchAndFinancialInstitutionIdentification6;
/**
* Set of characteristics shared by all individual transactions included in the message.
*/
@MessageComponent
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "GroupHeader85", propOrder = {"msgId", "creDtTm", "authstn", "nbOfTxs", "ctrlSum", "initgPty", "fwdgAgt"})
@Builder(toBuilder = true)
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)
@Data
@Description("Set of characteristics shared by all individual transactions included in the message.")
@Schema(description = "Set of characteristics shared by all individual transactions included in the message.")
public class GroupHeader85 implements Serializable {
public GroupHeader85() {
}
/**
* Point to point reference, as assigned by the instructing party, and sent to the next party in the chain to unambiguously identify the message.
Usage: The instructing party has to make sure that MessageIdentification is unique per instructed party for a pre-agreed period.
*/
@MetaData(fullName = "MessageIdentification", businessElement = "paymentIdentification.executionIdentification")
@XmlElement(name = "MsgId", required = true)
@NotNull
@Size(min = 1, max = 35)
protected String msgId;All Message Definitions and Message Components can be found in the following artifact
<dependency>
<groupId>com.iconsolutions.iso20022.model</groupId>
<artifactId>message-model</artifactId>
<version>${icon-iso20022-model.version}</version>
</dependency>